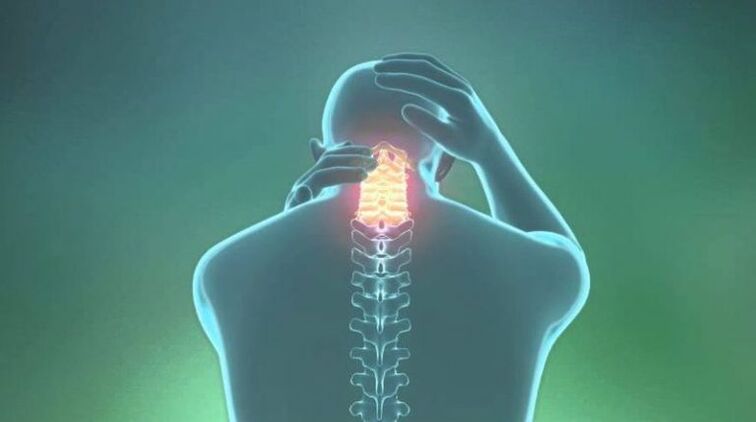
Osteochondrosis is one of the most insidious diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Its symptoms are often masked by other diseases and cause a lot of unpleasant and painful sensations. The appearance of pathological changes in the cervical spine is associated with the influence of various factors.
Symptoms
Cervical osteochondrosis is accompanied by a wide variety of symptoms. Headache, tingling in the center of the chest or chronic fatigue - all these signs accompany dystrophic disorders of the cervical vertebrae.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis:
- Vertigo, sometimes leading to unconsciousness or fainting.
- Crunch when you try to twist or turn your head.
- I draw pain and tingling in the shoulders, elbows or neck.
- Tingling in the arms and legs, from the fingertips and along the entire limb.
- Unreasonable aspect of apathy and drowsiness. The feeling of accumulated fatigue continues even after a long sleep or passive rest.
- Tinnitus (tinnitus with no apparent cause).
- Hearing loss or blurred vision.
- Pain in the sternum, with numbness in the hands or feet.
| Syndrome | It causes | Demonstration |
|---|---|---|
| Root | Compression of the spinal nerves. | Sharp pain on movement. |
| Reflex | Pinched nerve. | Sharp pain radiating to the arm, headache. |
| Compression-spinal | Pinching of blood vessels, intervertebral hernia. | Loss of sensation in the hands, pain in the shoulder girdle and neck. |
| Cerebral | Circulatory disorders of the spinal cord. | Tiredness, irritability and nervousness, disorientation and fainting, headaches and hearing problems. |
| Vertebral artery | Squeezing of the artery. | Stroke, cerebral ischemia. |
Important: The neck is one of the most important sections of the spine due to the accumulation of a large number of nerve trunks. Even a slight displacement of the vertebrae by 1-3 mm leads to a violation of the blood circulation of the brain and can cause hypertension, migraine. Less often at cerebral hypoxia, stroke.
Over the past 2 decades, doctors have noticed the appearance of osteochondrosis in young people. If earlier in the risk group there were representatives of middle and elderly age, at the moment the disease is increasingly common in people as young as 20-30 years old.
The danger of any symptoms of osteochondrosis lies in the fact that they are attributed to other diseases, and the appeal to specialized specialists is delayed. This makes it possible for the disease to become chronic and lead to irreversible damage to the anatomical structures of the cervical spine.
Causes of osteochondrosis
Each segment of the spinal column is built according to a single principle: the soft pulp inside the vertebra absorbs all the structures of the segment, loses its elasticity and ossifies. The pathological process affects the nerves and blood vessels.
To understand the causes of osteochondrosis, consider the problem from a medical point of view.
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| physiological process | Aging of cartilage tissue due to irreversible age-related changes. It is regulated by nervous and endocrine processes. |
| Pathological process | Destruction of vertebral structures, nerve endings and blood vessels. |
| Physiological changes | The transformation of the pulp into fibrous tissue, caused by the aging of the body. It does not manifest itself clinically if the nerve nodes are not irritated. |
| Pathological changes | Located in the cartilage and beyond, it irritates the nerves, compresses the blood vessels. Manifested by local pain and discalgia - a reflection of pain. |
Pathological changes in the vertebrae are accompanied by:
- Deposition of salts in the nucleus pulposus.
- Penetration of vertebral structures into neighboring segments (formation of hernias).
- Erasure and wear of segments of the cervical spine.
- Soft tissue ossification of the joints.
Causes of osteochondrosis:
- Autoimmune: Diseases lead to degenerative processes in the cartilage tissue.
- Infectious - the presence of pathogenic microorganisms leads to metabolic disorders in the tissues and can trigger pathological processes in the joints.
- Involutive - natural aging processes of the body.
- Traumatic - the development of pathologies as a result of injuries.
- Endocrine - hormonal disorders.
- Metabolic disorders - degenerative processes as a result of metabolic failures.
- Heredity - congenital pathologies of the development of the joints, cartilage. anatomical disorders.
- Stay in one position for a long time.
- Overweight - increases the load on the cervical region and can cause metabolic disturbances.
- Nervous strain and prolonged exposure to a stressful situation.
- Rheumatism.
Folk methods of treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Along with conservative medical methods, folk methods are highly effective in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Herbal treatment
Phytotherapy is widely used in osteochondrosis of the neck for many reasons: a small number of contraindications, availability, high efficiency, cumulative effect of the use of tinctures and decoctions.
Preparation of the decoctions
1 liter of water should be brought to an enameled bowl and add 5-6 tablespoons of the collection. Put the broth on a low heat and cook for about 15 minutes.
Alcohol tinctures of herbs such as wild rosemary, burdock, mountaineer, elecampane, sage, yarrow are used both for external use and for oral consumption. The principle of preparation of tinctures is as follows:
- 2-3 tablespoons of crushed plants are placed in a 250 ml container and medical alcohol is added
- the infusion is left to mature in a cool and dark place for at least 14 days. All of the above herbs are suitable for cooking.
Preparation of the infusion: pour 4-6 tablespoons of chopped vegetable raw materials into a 1 liter jar and pour boiling water over it. Cover the jar and leave for 24 hours in a dark place.
Tablets
The simplest method of treatment is the use of compresses of bischofite, saline. the high efficiency of the method is tested over time, the main principle of the treatment is regularity and long-term impact. Bandages made of soft cloth or a bandage are applied to the neck for a long time.
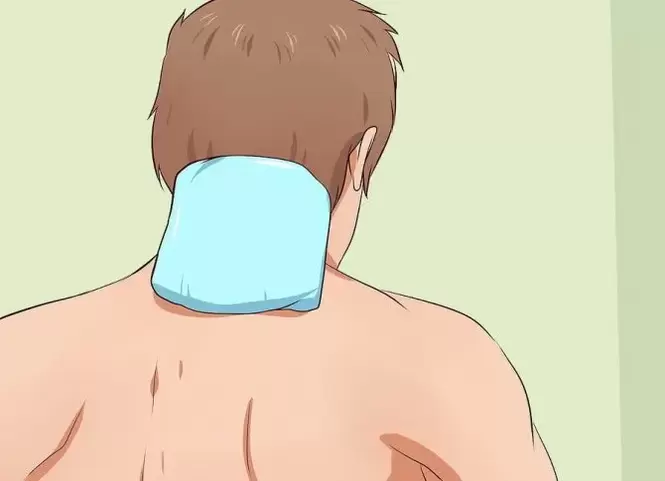
Salt pack: prepare a 10-11% saline solution (100g per 1000ml of water). Moisten the folded gauze in several layers in the resulting solution and apply to the neck. Put the polyethylene on top and wrap with a warm scarf. The compress should be done daily for about 10-14 days 1-2 times a day.
Ointments
You can fight cervical osteochondrosis with homemade ointments. For their preparation are used: herbs, vegetable roots, vegetable oils and animal products - fat, poisons, bile, eggs.
Ointment recipe:
- In equal proportions, mix the grass of yarrow, lavender, horsetail, dandelion roots (previously crushed).
- Pour 2-3 tablespoons of the collection with boiling water and put on low heat for 5 minutes, stirring constantly.
- After cooling, mix the resulting mixture with 75 g of any vegetable oil and 75 g of animal fat until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Rub on the neck for 4-5 minutes 2-3 times a day.
Rubbing
Rubbing will help relieve neck pain with osteochondrosis. The effectiveness of this method lies in the fact that it has a complex effect. Rub the neck with the use of tinctures and ointments is effective in exacerbations and complex therapy. Biologically active substances easily penetrate the tissues thanks to the mechanical effect on the skin.
Rubbing from the ointment (the recipe is given above): take a small amount of ointment and rub it into your palms. Then, with intense stroking movements, rub the ointment on the neck, after which it is necessary to isolate with a wool scarf. Perform the procedure for at least two weeks in a row 1-2 times a day.
heating
This method of exposure is used in cervical osteochondrosis to eliminate toxins accumulated in the cartilage tissue, improve blood and lymphatic microcirculation. Herbal baths, saunas, special hot plates, baked or boiled potatoes (in the form of mashed potatoes and honey cakes), bags of salt or sand are suitable for heating. After warming up, applying tinctures, ointments and compresses is most effective.
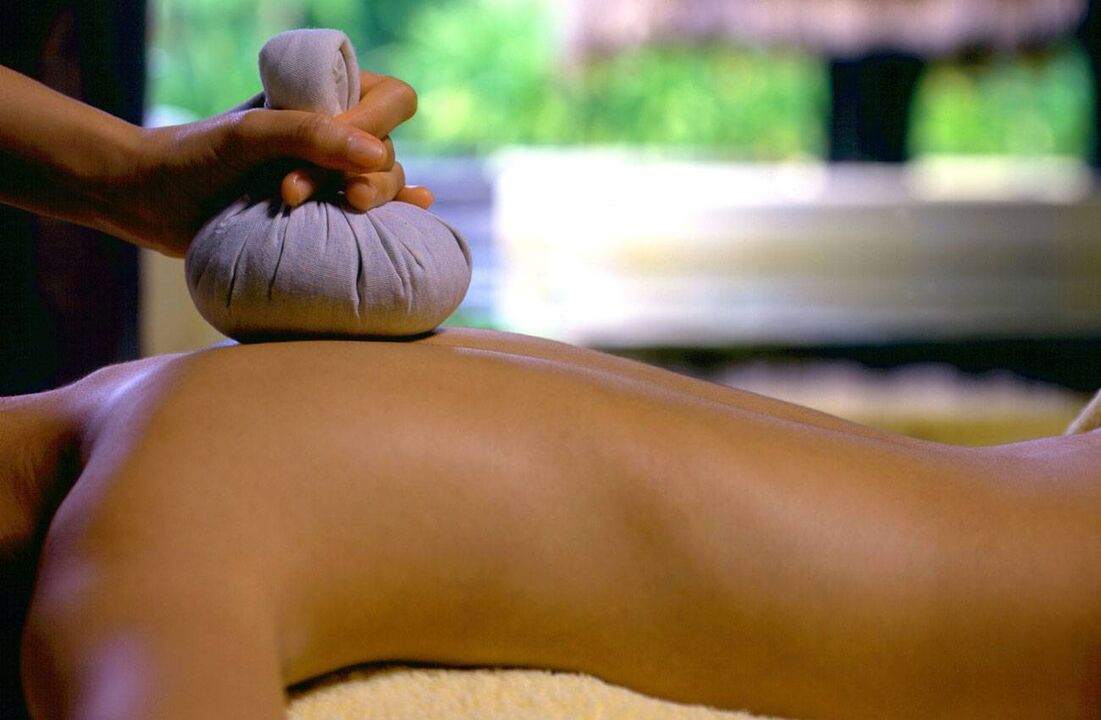

To warm up, you will need sea salt and a dense natural fabric bag, better than linen. Salt must be heated in a pan and pour the bag. Apply to the affected area 2-3 times a day. After the procedure, wrap your neck with a warm scarf and do not go out, especially in the cold season.
Massage
This method is used only during the period of remission, in the absence of sharp pains and other acute symptoms of osteochondrosis.
The healing properties of massage have been known for a long time and it is one of the best ways to remove osteochondrosis from the neck. Various massage techniques allow you to relieve spasm of the muscles surrounding the segments of the spine:
- acupressure;
- classic;
- Power;
- empty;
- Thai;
- self-massage.
This effect leads to an improvement in local blood circulation, relieving swelling, eliminating pain in the cervical region, improving tissue metabolism, restoring mobility of the cervical region and reviving atrophied muscles.
Self-massage for osteochondrosis is performed sitting or standing, the back is even, the feet are shoulder-width apart. You can use one or two hands for the following techniques:
- Rub the neck and neck area with your palms to warm up.
- Grab the neck with your hands so that your thumbs are in front and the rest from behind. In this position, hold four fingers from the spine to the periphery along the entire neck and collar area for 2-3 minutes.
- Circular movements with the fingers with pressure, covering as much as possible the surface of the neck. Continue 1-3 minutes.
- Vertical rubbing along the spine with the fingertips - 1-2 minutes.
Gymnastics for osteochondrosis
It is almost impossible to quickly cure osteochondrosis, but special exercises will help speed up the recovery process.
A set of exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine includes:
- Head rotations left and right: perform 5-6 repetitions in both directions, gradually increasing the amplitude.
- Raising and lowering the shoulders - 10-15 times.
- The head tilts left and right - 10-12 times in both directions.
- Stretching your head in front - in a standing position, stretch your head as far forward as possible, then return to its original position. Do 10-15 repetitions.
- Cobra: Get on all fours and gently stretch your head forward, aligning your legs and raising your head. Try to lower your hips to the ground. Lock in this position for a few seconds and slowly come back. Repeat 4-9 times.
The last exercise helps to relax the muscles of the cervical region, restore blood supply and eliminate pinching of blood vessels and nerve endings.
All exercises are performed slowly, smoothly and with a steadily increasing amplitude. The number of repetitions and approaches is determined individually.
Nutrition for cervical osteochondrosis
With damage to the joints, nutrition should be balanced and fractionated - 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Limit your intake of salt, simple carbohydrates, spicy and fried foods.
Foods with a high content of calcium, magnesium and phosphorus should be included in the diet - these are vegetables, fish, meat, stewed or baked vegetables.
To effectively combat cervical osteochondrosis, increase the intake of clean water (at least two liters per day).
Prevention
The disease is easier to prevent than to cure. To reduce the risk of osteochondrosis, take the following preventive measures:
- use a comfortable place to sleep - orthopedic mattresses and pillows;
- engage in regular physical activity;
- work in an adequately organized place on condition of sedentary work;
- with a static position of the body, take breaks for gymnastics;
- do not eat too much;
- do not carry bags on one shoulder.
Contraindications
The main contraindications are:
- physical overload from a long stay in a static position;
- deliberate crunching of the neck joints;
- consumption of a large number of sweets and starchy foods;
- weightlifting;
- sleep on a soft mattress and a large pillow;
- hypothermia of the cervical region.
Treatment of osteochondrosis should be complex. The combination of various means and methods of therapy, subject to recommendations on nutrition and physical activity, can relieve chondrosis of the neck. Despite the effectiveness of alternative treatment methods, seek help from an orthopedist or osteopath in time, as self-treatment can pose a health risk.



















